This is a step-by-step guide for installing a Bitcoin Core node as a Hot Wallet source for CAS. While you can operate a node on any suitable server, this guide is based upon a VPS using Digital Ocean. The intricacies of node installation (and operation) in a different environment are outside the scope of our support, and in such situations you should seek assistance from the Bitcoin Core community.
This guide is based on VPS installation only! |
Before you begin…The following example presumes you have the following ready:
|
It’s common for full nodes on high-speed connections to use 200 gigabytes upload or more a month. Download usage is around 20 gigabytes a month, plus around an additional 195 gigabytes the first time you start your node.
- https://bitcoin.org/en/full-node#minimum-requirements
wget https://bitcoin.org/bin/bitcoin-core-0.20.1/bitcoin-0.20.1-x86_64-linux-gnu.tar.gz |
Optional: verify the file integrity:
wget https://bitcoincore.org/bin/bitcoin-core-0.20.1/SHA256SUMS.asc gpg --list-keys gpg --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com --refresh-keys gpg --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 0x90C8019E36C2E964 gpg --edit-key 0x90C8019E36C2E964 trust |
Press 5 (“5 = I trust ultimately” ), and “y”:
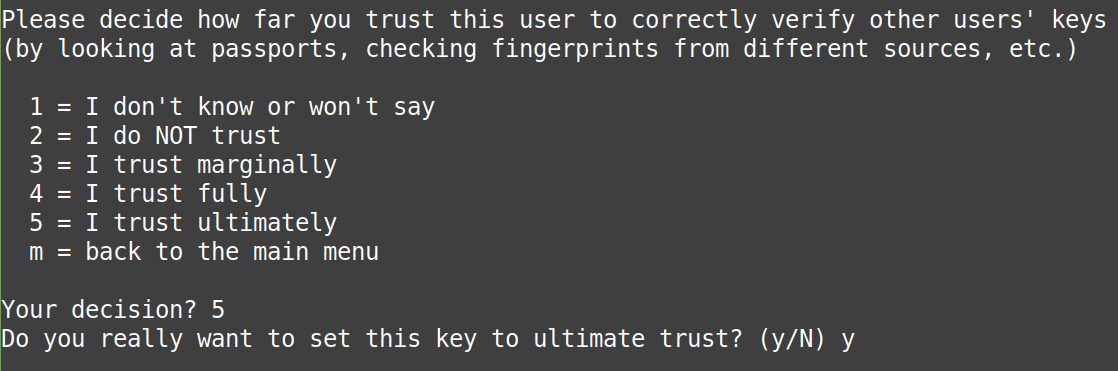
then type “quit” to exit gpg. Next, examine the signature:
gpg --keyid-format long --list-keys --with-fingerprint 0x90C8019E36C2E964 |
expect to see: "Key fingerprint = 01EA 5486 DE18 A882 D4C2 6845 90C8 019E 36C2 E964"
gpg --verify SHA256SUMS.asc |
expect to see: 'gpg: Good signature from "Wladimir J. van der Laan (Bitcoin Core binary release signing key) <laanwj@gmail.com>"'
sha256sum --ignore-missing --check SHA256SUMS.asc |
expect to see: "bitcoin-0.20.0.1-x86_64-linux-gnu.tar.gz: OK" .
ignore anything additionally reported by the last command.
tar xzf bitcoin-0.20.1-x86_64-linux-gnu.tar.gz |
sudo install -m 0755 -o root -g root -t /usr/local/bin bitcoin-0.20.1/bin/* |
The RPC token is designed to eliminate the need for hard-coded passwords in configuration and script files. You will receive a password here ONCE.
This password is required for CAS - it's your “RPC Password” noted in Step 6. |
sudo wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bitcoin/bitcoin/master/share/rpcauth/rpcauth.py -O /usr/local/bin/rpcauth.py |
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/rpcauth.py |
rpcauth.py AnyNameYouWantHere |
Replace AnyNameYouWantHere with any preferred user name.
Avoid using spaces or any special symbols.
The user name is required for CAS - it's your “RPC User” noted in Step 6. |
Example:
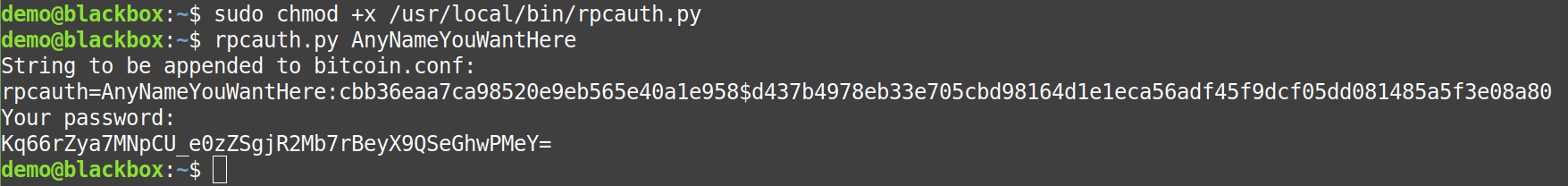
Save all the information securely. You'll need every detail in the steps to follow.
The RPC User = AnyNameYouWantHere
The RPC Password = Kq66rZya7MNpCU_e0zZSgjR2Mb7rBeyX9QSeGhwPMeY=
The cookie/token ("rpcauth") will only be required in the Bitcoin Core configuration file (next step).
The RPC Password is required for CAS - noted in Step 6. |
The cookie/token is a secure hash of your password. The point is to hide your password on the node server to other users of the node. If your node is secure, then using the cookie is simply added security in the event of a server breach, however if your server is breached - you have a bigger problem than an exposed password - and that hash will afford very little protection.
The password is sent to the RPC server software by CAS, and must be kept encrypted while traveling over the Internet. This is accomplished using “tunnels”.
The cookie/token is a secure hash of your password. The point is to hide your password on the node server to other users of the node. If your node is secure, then using the cookie is simply added security in the event of a server breach, however if your server is breached - you have a bigger problem than an exposed password - and that hash will afford very little protection.
The password is sent to the RPC server software by CAS, and must be kept encrypted while traveling over the Internet. This is accomplished using “tunnels”.
mkdir $HOME/.bitcoin touch $HOME/.bitcoin/bitcoin.conf chmod 0600 $HOME/.bitcoin/bitcoin.conf |
nano $HOME/.bitcoin/bitcoin.conf |
server=1 daemon=1 rpcport=8332 rpcauth=ThisIsAnExample:77cf8c03b15219cafb1e72ae9329d5fd$72de450660cdb6dd2689cd2cba4091646a5e8005490dec07dc577b6dad67770e |
Replace the “rpcauth” line with the cookie/token you generated in the previous step.
Exit the nano editor with Control+X and save your changes.
The CAS parameter “port” is the same as the “rpcport” specified in this step.
"When Bitcoin Core daemon first starts, it will begin to download the blockchain. This step will take at least several days, and it may take much more time on a slow Internet connection or with a slow computer."
bitcoind |
It may take several minutes for Bitcoin Core to completely start.
In actual practice, expect to wait 1-5 days for bitcoind to synchronize.
CAS will NOT be able to interact with bitcoind until the synchronization is COMPLETE!
To check the status, get the current block being processed by your node:
bitcoin-cli getblockcount |
Compare the returned number to the latest network block:
To STOP or interrupt Bitcoin Core at any time, use the following command:
bitcoin-cli stop |
It will resume downloading from the point where it stopped the next time you start it. It may take a few minutes to completely shut down.
The Bitcoin Core node (bitcoind) is now running. |
The tunnel must be live 24x7.
General Bytes has incorporated an open-source ssh client into CAS.
Click here for instructions to install the GB Wallet Tunnel Server.
The CAS “host” parameter used will be this node’s public IP.
The CAS “port” parameter will be the same port specified as the “rpcport” in Step 3 (above).
You may elect to use a SSH tunnel for secure RPC communication with the node. We also discourage running any software on your CAS server (except for CAS itself) and this includes Bitcoin Core. The solution is use port forwarding to enable access to your separate Bitcoin Core node. We recommend "dialing out" from CAS to the node.
The general usage would be:
ssh -f -N -i /home/gb/.ssh/bitcoind -L 8332:127.0.0.1:8332 gb@35.237.163.176 |
In the above example,
"ssh -f -N" is the "create a permanent tunnel in the background" command.
"-i /home/gb/.ssh/bitcoind" specifies the private SSH key to be used.
"-L 8332:127.0.0.1:8332" are the node's RPC port definitions.
"gb@35.237.163.176" is the SSH "dial-in" identity of the node.
user: this is the “RPC User” you invented earlier in Step 2.
password: is the “RPC Password” you also created earlier in Step 2.
Follow this link to see configuration instructions for Bitcoin Core with CAS. |
More information about the RPC API: https://developer.bitcoin.org/reference/rpc/index.html
Note: bitcoin-qt is NOT supported at this time. |
A "pruning node" (or lightweight node) is a special configuration that may be applied to bitcoind. It is unsupported by General Bytes. It is a substantial security risk when operating a BATM. Per the Bitcoin wiki:
“Lightweight nodes are sometimes able to be temporarily tricked into accepting transactions or blocks that are not actually valid. This could cause serious financial damage, especially for websites that automatically process Bitcoin transactions. Full nodes provide the maximum security possible, and so they should be used by all businesses, and also by regular users whenever doing so is convenient.”
- https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Full_node
The instructions given in this guide do not enable “pruning nodes”.
|
Backup is a matter of copying the wallet file normally located in $HOME/.bitcoin/wallet.dat .
The wallet.dat file can change over time because:
New Transactions: when you receive or send Bitcoin, new transactions are recorded in the wallet file.
New Addresses: if you generate new addresses for receiving Bitcoin are added to the wallet file.
Private Key Generation: new private keys (for new addresses) are stored in the wallet file.
A file backup would be the most comprehensive recovery option in the event of catastrophe. Since the file is so sensitive though, having multiple copies also increases your hack risks. Secure your backups!
It is not recommended to print or expose your private key, especially in a terminal or any other insecure environment. However, if you absolutely need to retrieve your private key for a specific address using bitcoin-cli, you can use the dumpprivkey command.
bitcoin-cli dumpprivkey "your_bitcoin_address" |
Replace "your_bitcoin_address" with the actual address for which you want to retrieve the private key. This command will output the private key associated with that address.
Be extremely cautious with this operation. Anyone with access to your private key can control your Bitcoin funds associated with that address. We generally recommended you use hardware wallets or other secure methods for managing your private keys.
The content by label feature displays related articles automatically, based on labels you choose. To edit options for this feature, select the placeholder below and tap the pencil icon.
|